Watery semen is a common condition, but most men don’t realize it because they rarely go for regular reproductive health check-ups. When this issue persists, sperm quality gradually declines, making it harder for couples to conceive naturally.
In fact, watery semen is one of the leading causes of male infertility. Understanding the causes early on helps men take timely action to protect their fertility and overall health.
What Is Watery Semen?
Normally, each ejaculation produces about 2–5 ml of semen, containing 60–80 million sperm per milliliter.
If both the semen volume and sperm concentration are below these levels, the condition is considered watery semen.
Depending on sperm count and quality, the condition can be classified as:
- Azoospermia: No sperm present in the semen
- Oligospermia: Sperm count < 20 million/ml
- Asthenozoospermia: Weak or immotile sperm
- Teratozoospermia: Abnormally shaped sperm
How to Recognize Watery Semen
Men can identify early warning signs such as:
- Semen that is thin, watery, or lacks the usual sticky, viscous texture
- Semen appears translucent or milky-white, resembling rice water, and may have a fishy odor
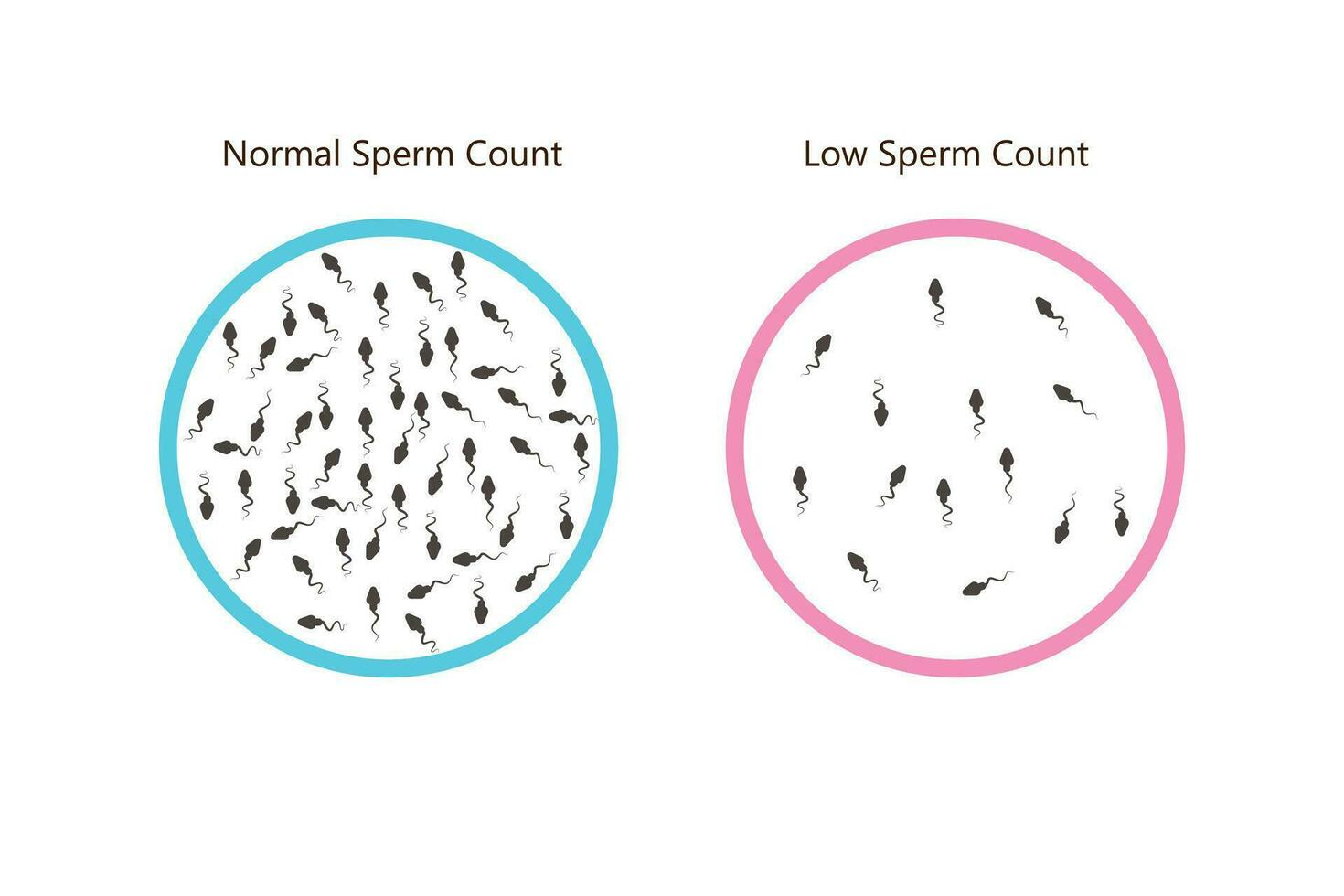
Watery semen usually comes with a low sperm count, one of the most common causes of male infertility — and should never be ignored.
Common Causes of Watery Semen
Watery semen may result from lifestyle factors, environmental influences, or medical conditions that affect sperm production.
1. Low Sperm Count
Normally, 1 ml of semen contains about 15 million sperm or more. Several factors can reduce this count:
- Infections: Bacterial infections such as epididymitis, gonorrhea, or syphilis can damage sperm or reduce sperm production.
- Varicocele: Enlarged veins in the scrotum impair testicular function, lowering testosterone and sperm count.
- Testicular tumors: Tumors interfere with sperm production and semen quality.
- Hormonal imbalance: Low testosterone reduces sperm production.
- Other causes: Autoimmune disorders, retrograde ejaculation, or genital trauma.
2. Congenital Defects
Conditions such as undescended testicles or testicular atrophy may lead to hormonal deficiency, poor sperm production, and infertility.
3. Excessive Sexual Activity or Masturbation
Frequent ejaculation depletes sperm reserves, leading to thinner semen. Over time, this can also weaken overall reproductive health.
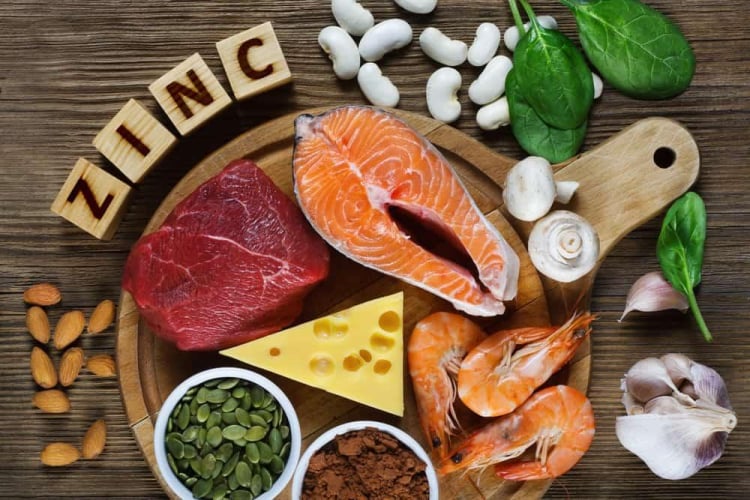
4. Zinc Deficiency
Zinc is essential for testosterone and sperm production. Low zinc levels result in reduced sperm count, lower libido, and weaker semen quality.
5. Other Risk Factors
In addition to the main causes, the risk of low sperm count in men can increase if there are risk factors such as:

- LAlcohol and Tobacco Abuse: Harmful substances found in alcohol and cigarettes — such as nicotine, carbon monoxide, methanol, and aldehydes — not only damage liver function and the digestive system but also negatively affect sperm production. Studies have shown that men who smoke regularly or frequently consume alcohol tend to have lower testosterone levels and reduced sperm count.
- Chronic Health Conditions: Watery or discolored semen can also result from chronic diseases such as diabetes, gout, hypertension, or even cancer. These conditions can disrupt hormone balance and impair the reproductive process.
- Chronic Stress: Testosterone is produced in the testes but regulated by the hypothalamus and pituitary gland. When the nervous system is under prolonged stress, these glands become suppressed, leading to decreased hormone production and lower sperm count.
Diagnosis: How to Know for Sure
A semen analysis (sperm test) is the most reliable way to evaluate sperm health — measuring sperm count, movement, and morphology.
Doctor may also recommend hormonal tests (testosterone, FSH, LH) to assess underlying causes.
Can Men with Watery Semen Still Have Children?
Many men with watery semen have a low sperm count, which makes natural conception more difficult.
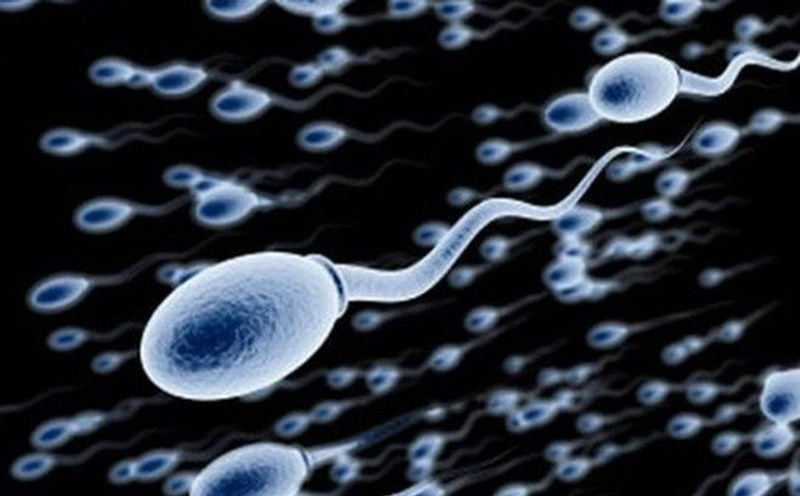
A low sperm concentration in semen is one of the leading causes of male infertility.
While it only takes one sperm to fertilize an egg, millions of sperm per milliliter of semen are needed to increase the chances of conception.
When semen volume and sperm count are both low, a man’s likelihood of becoming a father significantly decreases.
However, difficult does not mean impossible. Many men with watery semen or low sperm count can still achieve fatherhood with the right treatment approach.
In addition to lifestyle changes and medical therapy, modern reproductive technologies such as IUI (Intrauterine Insemination) and IVF (In Vitro Fertilization) have helped numerous couples overcome infertility — even when the male partner has poor sperm quality.
Thanks to these advancements, many men have been able to fulfill their dream of becoming fathers.
Treatment for Watery Semen
Treatment depends on the underlying cause and may include:

1. Medication
- Other targeted treatments: For congenital or structural issues
- Zinc supplements: For men with nutritional deficiencies
- Antibiotics: If infections are present
- Other targeted treatments: For congenital or structural issues
Surgery
In cases involving varicocele or genital abnormalities, surgery can restore normal sperm production.
Lifestyle Modifications
Men need to eliminate bad habits that affect their health and sperm quality.
- Quit smoking and limit alcohol
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Practice safe and moderate sexual activity (2–3 times/week)
- Exercise regularly
What to Eat to Improve Sperm Quality

A balanced diet plays a key role in improving sperm count and quality:
- Zinc-rich foods: Zinc is essential for healthy sperm production. Make sure to include zinc-rich foods in your diet such as beef, oysters, shrimp, and pumpkin seeds to support fertility.
- Foods high in lycopene: Lycopene is the red pigment found in fruits like tomatoes and watermelons. According to experts, lycopene may help improve sperm quality, count, and motility — key factors for successful conception.
- Antioxidant-rich foods: Antioxidants protect sperm cells from damage caused by free radicals, helping maintain sperm health. They can be found in a variety of fruits and vegetables such as raspberries, blueberries, oranges, grapefruits, artichokes, asparagus, cabbage, and black beans.
- Foods rich in L-carnitine: L-carnitine plays an important role in boosting cellular energy and enhancing sperm production. It helps sperm cells stay healthy and improves fertility outcomes. L-carnitine is abundant in lean pork, chicken breast, poultry, fish, and mushrooms.
Zplus – The Men’s Health Solution for Sperm Quality
In addition to lifestyle and habit changes, men can also consider using nutritional supplements to improve sperm quality — such as Zplus.
Zplus is the first product developed under the Men’s Health brand.
It represents our dedication to creating high-quality products designed specifically for Vietnamese men — with the goal of helping them receive the best possible care for their reproductive health.
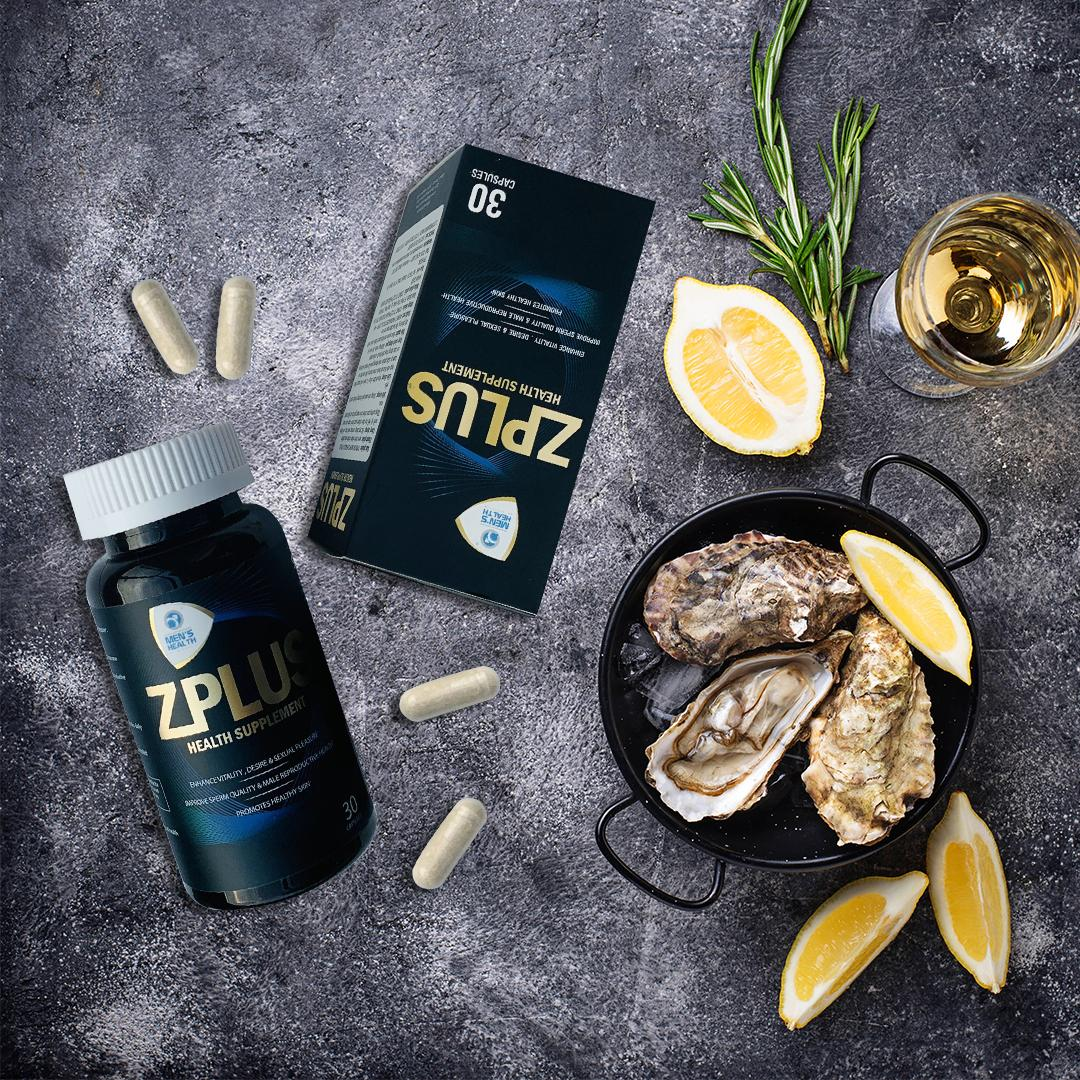

Zplus is a combination of oyster extract and essential minerals such as zinc and selenium, all of which play key roles in supporting male fertility.
Key Benefits of Zplus
1. Oyster Extract – A Natural Source of Vitality
Oysters are known as a “food for happiness” thanks to their exceptional nutritional value for men’s health — benefiting cardiovascular function, sexual performance, blood circulation, and muscle strength.
From a medical perspective, oyster meat is rich in essential minerals and vitamins, particularly zinc (Zn), which is crucial for sperm production.
It also provides protein, carbohydrates, healthy fats, magnesium, calcium, manganese, iron, phosphorus, vitamin D, and B-group vitamins, all of which support metabolism and overall vitality.
As a result, oyster extract can:
- Enhance male sexual performance by improving sperm count and quality, helping reduce erectile dysfunction, premature ejaculation, and related issues.
- Support cardiovascular health by lowering bad cholesterol and improving blood vessel elasticity.
- Boost blood circulation and oxygen delivery to the penile tissue, aiding in the management of erectile dysfunction.
- Strengthen muscles and brain function through nutrients like omega-3, taurine, and trace elements.
2. Zinc – The Foundation of Male Fertility
Zinc is an essential mineral for reproductive organ development, motor function, and cognitive health.
It also plays a crucial role in prostate function and sperm formation.
Zinc deficiency can lead to infertility and prostate-related disorders.
When used in the right dosage, zinc supplementation helps support reproductive health and hormone balance — but excessive intake should be avoided.
3. Selenium – Enhancing Sperm Motility and Fertility
Selenium contributes to sperm motility and improves blood flow, both of which are essential for conception.
It is incorporated into the mitochondrial membrane of sperm cells, influencing their movement and function in the female reproductive tract.
Some studies have also shown that selenium may help reduce the risk of miscarriage, though current research primarily focuses on its role in male infertility.
The Zplus formulation has been carefully developed to match the biological needs of Vietnamese men, ensuring optimal absorption and effectiveness.
Men’s Health specialists recommend taking 1–2 Zplus capsules daily for at least 3 to 6 consecutive months to achieve the best results.
The above information provides a comprehensive overview of watery semen and male infertility concerns.
If you have any questions or need personalized advice, please don’t hesitate to contact our hotline at 0911 161 161 for free consultation.
At Men’s Health, we are committed to providing accurate, compassionate, and effective care for every aspect of men’s health — with the motto:
“KNOWLEDGE – CARE – CONFIDENCE.”